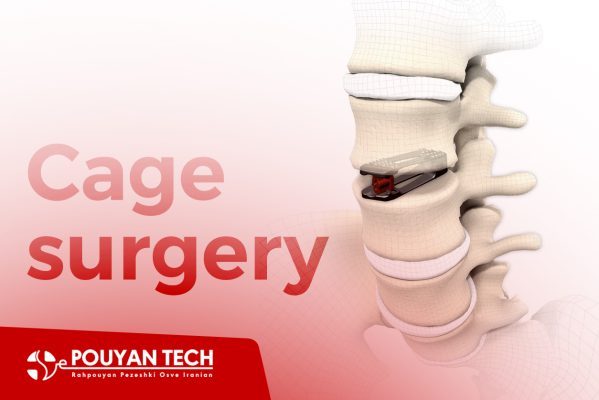
Cage surgery, also known as interbody fusion, involves the insertion of a small cage or spacer between two adjacent vertebrae in the spine. This procedure is commonly used to treat conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, or spinal instability. Here are the general steps involved in cage surgery between the vertebrae of the human spine:
1. Preoperative Evaluation: Before the surgery, the patient undergoes a comprehensive evaluation, including a physical examination, imaging studies (such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI), and potentially other tests to assess the condition of the spine and identify the specific areas requiring treatment.
2. Anesthesia: The patient is brought into the operating room and given anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free during the procedure. The type of anesthesia used will depend on the specific surgery being performed and the patient’s individual medical history.
3. Incision and Exposure: Once the patient is under anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the skin over the affected area of the spine. The muscles and other tissues are carefully moved aside to expose the bony structures of the spine.
4. Removal of Disc Tissue: The surgeon removes the damaged or degenerated intervertebral disc tissue between the vertebrae, creating space for the insertion of the cage.
5. Cage Insertion: Using specialized surgical instruments and guidance from fluoroscopy or intraoperative imaging, the surgeon carefully prepares the intervertebral space and inserts the cage between the vertebrae. The cage is typically made of a biocompatible material, such as titanium or polyetheretherketone (PEEK), and is available in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different spinal conditions.
6. Bone Graft Placement: In many cases, a bone graft material is placed within the cage to promote the fusion of the adjacent vertebrae over time. The bone graft can be sourced from the patient’s own bone (autograft) or from a donor (allograft), or it may be a synthetic bone graft substitute.
7. Closure: After the cage and bone graft are placed, the surgical site is thoroughly irrigated to remove any debris or bone fragments. The muscles and soft tissues are carefully repositioned, and the incision is closed with sutures or staples.
8. Postoperative Care: Following the surgery, the patient is monitored in the recovery area and then transferred to a hospital room or a postoperative care unit. Depending on the specific procedure and the patient’s condition, the recovery process may involve physical therapy, pain management, and other supportive measures to aid in healing and rehabilitation.

It is important to note that cage surgery between the vertebrae of the human spine is a highly specialized procedure and should only be performed by a qualified and experienced spine surgeon. The decision to undergo spine surgery should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider after a thorough evaluation and consideration of all treatment options. As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with spine surgery, so patients should discuss the procedure thoroughly with their healthcare provider before making a decision